AMOLED display (Active-matrix organic light-emitting diode)
 |
| Samsung is the largest Manufacturer of AMOLED displays |
- What is an LCD display
- What is an OLED
- How does an OLED works
- Types of OLED display
- AMOLED(Active) and Passive matrix OLED displays
- Advantages and disadvantages of AMOLED display
- Super AMOLED display
Expansion of AMOLED is Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode.Let us see what each term means.Let us start with LED.
LED Display
An LED display is a flat panel display, which uses an array of light-emitting diodes as pixels for a video/picture display.As you know an LED( light-emitting diode) is a p-n junction which emits light when electric current is passed through it.In an LED dispaly panel , these LEDs are shrunk down dramatically and arranged in red, green and blue clusters to create an individual pixel that can reproduce white light and various colors.
LED V/s LED back-lit LCD
LED displays are used in large displays like leaderboards,advertising pannels etcc. LED TVs and Smartphones displays are usually LCD with LED back-light. Usually consumers think that LED TVs have LED display. It is LED backlit LCDOLED Display
The O part in OLED stands for organic.In an OLED, a thin layer of organic material is placed between two conductors, which is then used to produce light when a current is applied.At least one of these electrodes is transparent.Properties of these organic material is analogous to semiconductors.
Working principle of OLED
Originally, the most basic polymer OLEDs consisted of a single organic layer.But modern OLEDs incorporate a simple bilayer structure, consisting of a conductive layer and an emissive layer.
During operation, a voltage is applied across the OLED electrodes such that the anode is positive with respect to the cathode.Current flows through the device from anode to cathode(direction of electrons flow is opposite to current direction).Emmissive layer is more negative(electrons are the majority carriers) and conductive layer is more possitive(holes are the majority carriers).
As more electrons are injected into emmissive organic layer(2) at the cathode(1) and withdrawn from conductive layer (4)at the anode(5). Electrostatic forces bring the electrons and the holes towards each other and they recombine. This happens closer to the emissive layer, because in organic semiconductors holes are generally more mobile than electrons. The decay of this excited state results in a relaxation of the energy levels of the electron, accompanied by emission of radiation whose frequency is in the visible region. The frequency of this radiation depends on the band gap of the material.
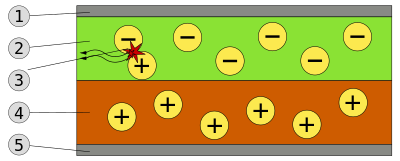 |
| Schematic of a bilayer OLED: 1. Cathode (−), 2. Emissive Layer, 3. Emission of radiation, 4. Conductive Layer, 5. Anode (+) |
Classification of OLED Displays
OLED displays can be classified into passive matrix OLEDs(PMOLEDs) and active matrix OLEDs (AMOLEDs) based on their driving circuit.In a passive matrix, a complex grid system is used to control individual pixels, where integrated circuits control a charge sent down each column or row. But this is rather slow and can be imprecise. Active Matrix systems attach a thin film transistor (TFT) and capacitor to each LED.Each OLED pixel can be accessed by activating corresponding row and column , allowing for faster and more precise control.
| Active v/s Passive matrix OLED |
Pros and Cons of AMOLED Displays
Pros
IPS display is the main competitor of AMOLED display.Samsung is the leading promoter of AMOLED displays.But many leading brands like iPhones and HTC still use IPS display.So here we are analyzing the Pros and Cons of AMOLED Displays in comparison with IPS Displays
- The panels are thinner: Allows for slimmer devices. AMOLED displays are much thinner than IPS Displays.
- IPS LCD displays need back-lighting.But LED pixels in AMOLED display produce light their own.
- Intense black color:In AMOLED display each pixel can be completely switched off,this in turn produces pure black colour.
- High Battery Life: An AMOLED consumes less power than IPS.
- High Contrast: AMOLED provide better contrast ratios.
Cons
- Expensive production: The technology needed to develop AMOLED panels is very expensive.
- Organic materials have limited lifespan, far shorter than the lifespan of LED or LCD. lifespans of each colour-specific organic material varies. Red and green OLED films have longer lifespans compared to blue OLED films. This variation results in colour shifts as a particular pixel fades faster than the other pixels.
- Low definition images: less sharper images
- Less accurate white colour when compared with IPS display
- Compared with an LCD, an AMOLED display is difficult to view in direct sunlight due to reduced maximum brightness and lack of backlighting
Super AMOLED displays
An AMOLED touchscreen usually has an extra, touch sensitive layer on top of the screen, but with Super AMOLED designers able to integrate touch sensitivity into the screen itself.This was designed by Samsung.The result of this is that not only is the screen thinner, lighter, more touch sensitive and less power-hungry, but without that extra layer it's also far less reflective than a typical AMOLED screen, making it easier to view in bright sunlight.
Phones with amoled display
Apart from Samsung, many leading smartphone manufactures have started opting AMOLED displays for their latest model.Here you can find some leading smartphones with AMOLED display.
- Huawei Mate 9 Pro
- One Plus 3
- Huawei Enjoy 6
- ZTE Axon 7 mini
- Asus Zenfone 3 Deluxe
- Samsung J1 2016
- Samsung W2017
- Honor Note 8
- Samsung Galaxy Note 7
- Xiaomi Mi Note 2
- Oppo F1 Plus
- lenovo Moto Z
- Meizu Pro 6
- Google Pixel / Pixel XL
- Vivo Xplay 5
- Samsung Galaxy C9 Pro
No comments:
Write comments